MapInfo Professional can connect to various RDBMS and store the spatial data in the database. In order to enable this feature, we need to create Mapinfo_Mapcatalog in the database. The mapinfo_mapcatalog is a special system table used by MapInfo Pro, particularly when you are working with spatial data stored directly in a remote database (like SQL Server, Oracle, or PostGIS). In this article, we will show you how to create this mapinfo_mapcatalog table. So if you are going to store the spatial datasets (points, line, and polygons) in the database, we need to create mapinfo_mapcatalog table in the database.
There are several ways to create mapinfo_mapcatalog. We can create this table from the Mapinfo program or we can also create this table from the database itself.
Using the MapInfo Easy Loader
Easy Loader is a mapbasic tool that can be used to create mapinfo_mapcatalog. To run this tool, go to Home | Tool Extensions. And then look for MapInfo EasyLoader. Double-click it to run.
In the EasyLoader window, choose create a new connection and then give a name for the new connection and choose the ODBC connection. FYI, you will need to create the ODBC connection to your database prior doing this step.
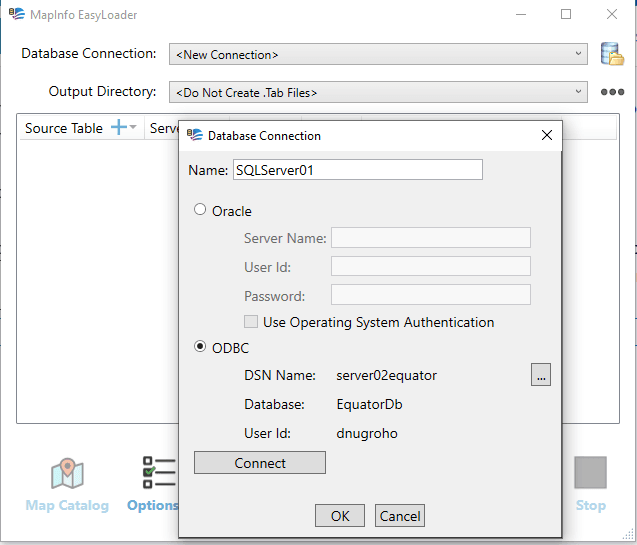
Click Connect and then OK. Next, click MapInfo Mapcatalog button to create the table.
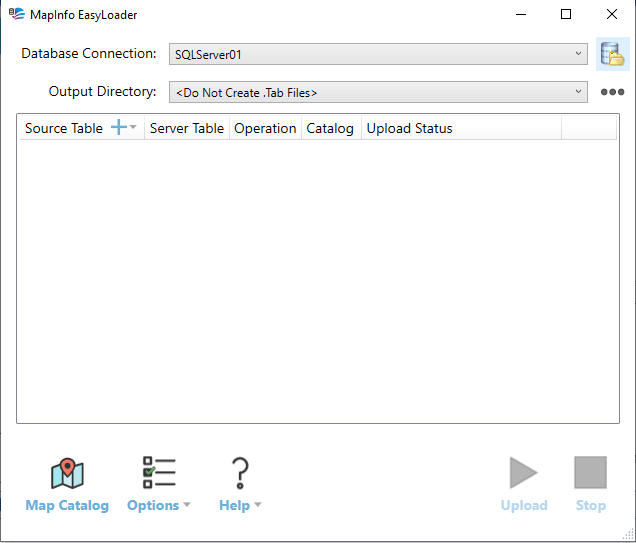
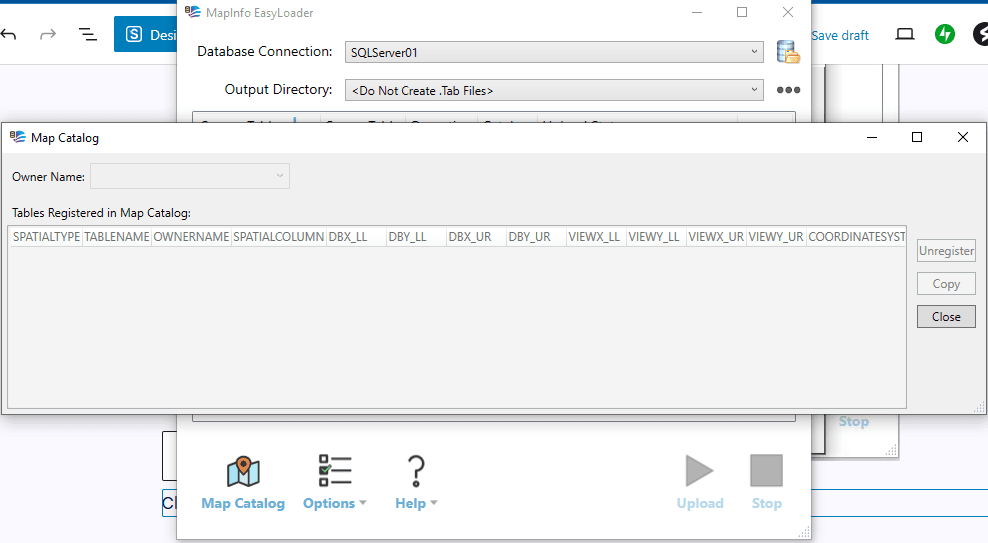
Now you have the Mapinfo Mapcatalog table in your database and you can start uploading the spatial data to the database.
Create mapinfo_mapcatalog Directly in the Database
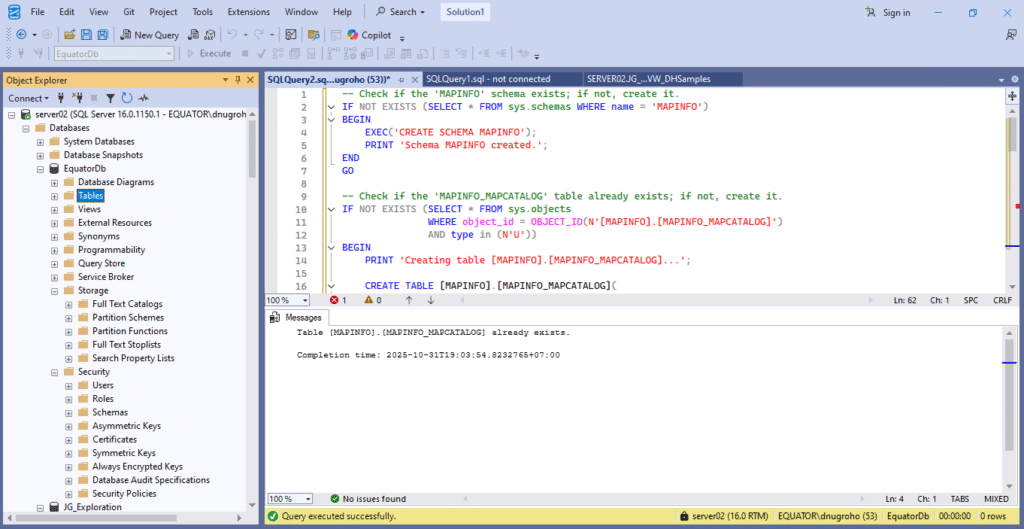
We can also create this catalog table directly in the database. If you are using Microsoft SQL Server, you can use this query script in your database. Just copy this line of codes in your SQL editor in MS SQL Server.
— Check if the ‘MAPINFO’ schema exists; if not, create it.
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.schemas WHERE name = ‘MAPINFO’)
BEGIN
EXEC(‘CREATE SCHEMA MAPINFO’);
PRINT ‘Schema MAPINFO created.’;
END
GO
— Check if the ‘MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG’ table already exists; if not, create it.
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[MAPINFO].[MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG]’)
AND type in (N’U’))
BEGIN
PRINT ‘Creating table [MAPINFO].[MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG]…’;
CREATE TABLE [MAPINFO].[MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG](
[SPATIALTYPE] [float] NULL,
[TABLENAME] [varchar](128) NOT NULL,
[OWNERNAME] [varchar](128) NOT NULL,
[SPATIALCOLUMN] [varchar](128) NULL,
[DB_X_LL] [float] NULL,
[DB_Y_LL] [float] NULL,
[DB_X_UR] [float] NULL,
[DB_Y_UR] [float] NULL,
[VIEW_X_LL] [float] NULL,
[VIEW_Y_LL] [float] NULL,
[VIEW_X_UR] [float] NULL,
[VIEW_Y_UR] [float] NULL,
[COORDINATESYSTEM] [varchar](254) NULL,
[SYMBOL] [varchar](254) NULL,
[XCOLUMNNAME] [varchar](128) NULL,
[YCOLUMNNAME] [varchar](128) NULL,
[RENDITIONTYPE] [int] NULL,
[RENDITIONCOLUMN] [varchar](128) NULL,
[RENDITIONTABLE] [varchar](128) NULL
);
PRINT ‘Table [MAPINFO].[MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG] created.’;
— Create the standard unique index on TABLENAME and OWNERNAME
PRINT ‘Creating unique index on [TABLENAME, OWNERNAME]…’;
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX [mapcatalog_idx]
ON [MAPINFO].[MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG] ([TABLENAME], [OWNERNAME]);
PRINT ‘Index created successfully.’;
— Grant permissions to public role so all users can read/write to it.
— Adjust as needed for your security policies.
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON [MAPINFO].[MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG]
TO public;
PRINT ‘Permissions granted to public role.’;
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT ‘Table [MAPINFO].[MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG] already exists.’;
END
GO